Citation: Oakley T, Saaler-Reinhardt S, “Development of a New High-Performance Autoinjector”. ONdrugDelivery Magazine, Issue 105 (Feb 2020), pp 14-17.
Tom Oakley and Sigrid Saaler-Reinhardt discuss the development of the Midas Pharma’s NIS cartridge-based autoinjector.
Prefilled syringes have become the standard format for delivering new biologic drugs. However, they suffer from various issues, such as:
- People do not like seeing needles.
- There is a risk of contamination and injury via needlesticks.
- They can be unsuitable for self-injection by people with hand tremors or dexterity issues from rheumatoid arthritis and suchlike.
- The force required to deliver viscous drug formulations through an acceptably thin needle could be too high either for the user or for the syringe.
- The drug formulation can interact with the silicone lubricant, the steel needle, the adhesive used to attach the needle or the tungsten used to form the hole for the needle.
Most spring-powered devices cause an impact when the spring is released. This could be avoided entirely if the spring was already pushing on the plunger, thus pressurising the drug during storage.
“Standard” autoinjectors, which are based on a compression spring pushing on the plunger of a prefilled syringe, can solve the first three issues. But the fourth issue is a growing challenge for standard autoinjectors because certain biologics – notably monoclonal antibodies – need to be administered in high concentration for subcutaneous self-administration. This can lead to an increased viscosity of the formulation, which requires greater spring force.
Most autoinjector designs hold the plunger rod back away from the plunger when the device is in storage. When the device is triggered, the plunger rod accelerates forward rapidly until it impacts the plunger and creates shock through the system which can break the syringe. Another source of impact is where some device designs insert the needle into the patient using the main power spring. This can accelerate the syringe forward at high speed and cause impact when the syringe is decelerated again.
There are some innovative devices tackling these problems – such as the Oval Medical (Cambridge, UK) ArQ-Bios, which uses a custom primary drug container, or the Consort Medical (Hemel Hempstead, UK) Syrina AS, which uses a liquified gas propellant in place of a spring. Both have their merits but require the pharmaceutical company to support either a non-standard primary drug container or a non-standard power source, respectively.
Another way to manage the increasing viscosity is to dilute the formulation back to a more reasonable viscosity and deliver a larger-volume injection. Several platform autoinjectors are now available in 2.25 mL syringe formats. However, the change from the 1 mL to the 2.25 mL syringe formats tends to require substantial changes to the device. Changing the computer-aided design (CAD) models and manufacturing a new set of tools for almost all components entails an increased risk, time delay and cost. Further, in general, they cannot support injections greater than 2.25 mL.
There is, therefore, the need for a new autoinjector which:
- Avoids the problems associated with prefilled syringes (drug interaction, limited volume, etc)
- Uses a standard primary container that is already widely used widely for injections
- Uses well-proven components (springs, needles, packaging, etc) that are already derisked and low cost
- Can deliver higher volumes and/or viscosity than other low-risk autoinjectors.
WHY USE A CARTRIDGE IN AN AUTOINJECTOR?
Pharmaceutical cartridges are widely used to deliver drugs such as insulin, fertility hormones and growth hormone. They differ from the staked-needle syringe in that cartridges have an elastomeric septum seal at one end rather than a needle. Also, cartridges do not have the flange seen on syringes. The main differences relevant to this discussion are summarised in Table 1.
| Syringe | Cartridge |
| ✘ Limited volume ✘ Fragile flange and shoulder ✘ Tungsten and adhesive around needle ✘ “Wet” needle in storage ✘ Sprayed-on silicone oil ✔ Used in early clinical trials |
✔ Volume limited only by length ✔ No flange, and a strong shoulder ✔ No tungsten or adhesive around needle ✔ No needle contact in storage ✔ Baked-on silicone oil ✘ Not typically used in early clinical trials |
Table 1: Comparison of syringes and cartridges.
Cartridges are not typically used in early clinical trials for many new biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies. However, they could be used by either fitting an adapter to add a needle and plunger rod or by using the autoinjector that we will introduce in this article.
WHY PRESSURISE THE DRUG IN STORAGE?
Most spring-powered devices cause an impact when the spring is released. This could be avoided entirely if the spring was already pushing on the plunger, thus pressurising the drug during storage. The advantages of this approach are:
- Impact is avoided, so stronger springs can be used without risk of impact breakage, which in turn means that higher viscosity and/or larger volumes can be delivered through a given needle diameter.
- Air bubbles have been shown to cause degradation of proteins (Christian Dechant, SMi Prefilled Syringes Europe Conference, London, UK, January 17-18, 2018). When the drug formulation is pressurised in storage, air tends to dissolve into the solution. In addition, any remaining bubbles are compressed, thus reducing their surface area available for interaction with the drug formulation.
- The plunger does not move when ambient air pressure is changed, for example during air freight.
- The triggering mechanism can be very simple and completely independent of the rear end of the autoinjector. The injection can be started by inserting a needle through the cartridge’s septum seal.
But could storage under pressure damage the drug? Testing at a pharma company has shown that there has been no degradation in their drug when stored at maximum pressure over the three-month period studied. There is no reason to believe there will be a different effect with longer duration. In fact, the reduction in bubble number and volume discussed above should reduce degradation.
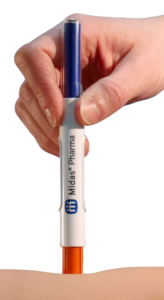
Figure 1: 3 mL NIS autoinjector.
THE NIS AUTOINJECTOR
The NIS autoinjector from Midas Pharma (Figure 1) is a cartridge-based autoinjector wherein the spring is always pushing on the plunger. The simplicity of the NIS design (Figure 2) means that:
- A 1.5 mL or 3 mL cartridge can be used with only minor changes. For example, the same tool could be used for the main body, which is unique amongst autoinjectors.
- For a given cartridge diameter, a change in drug volume or viscosity needs only a change in the spring and plunger rod length.
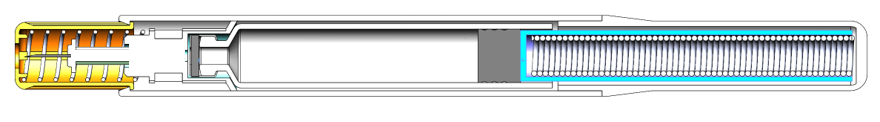
Figure 2: Section view of NIS autoinjector.
Figure 3 shows two use steps for the NIS autoinjector. However, the design is so simple that it is even possible to do away with the step of removing a cap, which would make the NIS autoinjector the first “one-step” autoinjector on the market.
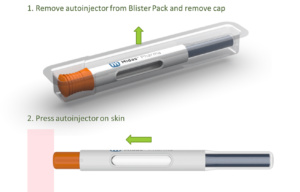
Figure 3: Use steps for NIS autoinjector.
HOW CAN WE PREDICT AUTOINJECTOR PERFORMANCE?
Our primary considerations are that the autoinjector should:
- Be safe – which means, for example, a low chance of breakage or underdose.
- Deliver the drug through a thin needle in a reasonable time.
In order to answer the second point, we would like to know the maximum viscosity each autoinjector design can deliver through a given needle gauge in the maximum allowable injection time limit. The injection time is dominated by the drug formulation being pushed through the needle. Flow through the needle is governed by the Hagen-Poiseuille equation:
![]()
Rearranging to calculate injection time gives:
![]()
Where Q is flow rate, π = 3.141, ΔP is the pressure drop, d is the needle inner diameter, μ is the dynamic viscosity, L is the needle length, t is the injection time, V is the drug volume, D is the syringe inner diameter and F is the force on the drug (which is spring force minus any friction).
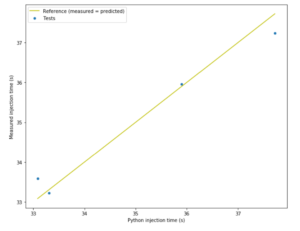
Figure 4: Actual injection times versus predicted injection times.
Figure 4 shows the correlation between measured injection time and predicted injection time for an example autoinjector filled with calibrated 50 cP silicone oil, with an extra thin needle and weak spring to give greater injection time than the real device. The difference between measured and predicted injection time is not more than 1.5% so the model is good enough for our purposes.
HOW DOES THE NIS AUTOINJECTOR COMPARE WITH COMPETITORS?
We could use the equation above to calculate the maximum viscosity which each autoinjector can inject in a given time through a given needle diameter – but that would assume that every parameter was at its mean value and would take no account of variation. Also, we want all injections to be under a given time limit – so we care about the slowest injections, not the mean. We need to calculate the distribution of injection times.
We could use algebraic manipulation but this is challenging and would become very challenging if any of the input distributions were not Gaussian. Instead, we can use a Monte Carlo simulation. For those who are not familiar with this method, the steps are:
- Model the distribution of each input to the equation (drug volume, needle diameter, etc).
- Take one sample at random from each input distribution.
- Calculate one output value by putting the sample input values through our equation.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until we have a suitably large number of output samples to represent the output distribution.
The validity of the Monte Carlo method depends on several factors being true:
- The inputs must be independent. For example, the needle diameter should not correlate with the needle length.
- The inputs should be representative. We have made our best efforts to use industry-wide tolerances and international standards.
Spring Force
- Each device platform has limited space for the spring.
- We calculated the strongest spring we thought could be designed into the space allowed.
- We used the industry standard tolerance of ±10% on spring force.
Device Friction and Plunger-Cartridge Friction
- Nominal friction was measured from device samples.
- Tolerance was estimated at ±70% (which approximates measurements from similar device developments).
Container Diameter
- Nominal diameter was measured from device samples.
- We matched the diameter to the nearest standard glass tube and used ±0.1 mm from ISO 13926-1:2004.
Needle Length
- Nominal was measured from device samples.
- Tolerance of ±1 mm was used because ISO 7864:2016 specifies maximum +1 mm and -2 mm.
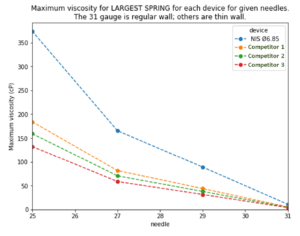
Figure 5: Maximum viscosity for the LARGEST SPRING for each device for given needle gauges. (The 31 gauge is regular wall, others are thin wall.)
We used the Monte Carlo method to calculate the maximum viscosity that could be injected by the NIS autoinjector and three competitors for various needle gauges, with no more than 1% of injections taking more than 15 seconds. The results (Figure 5) show that the NIS autoinjector could inject significantly higher-viscosity drugs than competitor devices. Alternatively, a similar viscosity could be delivered by the NIS through a smaller needle than competitors. Competitor devices would probably have unacceptable risks, such as plastic creep or glass impact, if they used the maximum force spring that could fit.
SUMMARY
There are demonstrable advantages to using a cartridge over a syringe in an autoinjector, as described in Table 1. Furthermore, pressurising the drug in storage can eliminate impacts and reduce drug degradation. Elimination of impacts means that the autoinjector could be designed to deliver higher viscosities and/or volumes than competitors that are on the market. The NIS autoinjector embodies these ideas in a simple and low-risk design.

